Trade Finance facilitates domestic and international trade transactions by providing capital for import and export activities.
Corporates and SMEs can access a wide range of financial products to support their growing business needs.
The following is a guide for those new to the market.
![]() Highlights of this article:
Highlights of this article:
- Importance of Trade Finance
A risk mitigation tool for importers and exporters - Who are the Different Trade Finance Players?
Know how financiers, introducers, and brokers connect borrowers - Who Can Access Trade Finance Solutions?
Industries and businesses best suited - How Can Trade Finance Facilitate Your Business?
The 6 main trade finance products explained
Content
Why do Companies Need Trade Finance?
Trade finance protects importers and exporters from counterparty risks. This could be a default from any party involved.
The importer needs to pay the supplier cash advance for goods to be shipped, while the exporter needs this capital as a security to avoid the risk of non-payment.
The 2021 trade finance company default shows how poor risk management changed the fate of a company.
International shipping is a complex process involving several risks. Read our article defining the 10 specific risks to unravel the many types of risks faced by businesses.
It is a standard practice in domestic and international trade to sell on payment terms. Thus, allowing the buyer (the debtor) to delay the payment of the invoice. Trade finance solutions help mitigate cash flow imbalances due to these payment gaps.
For example, the shipping of goods can take several weeks before reaching the purchaser’s warehouse. This gives the buyer a perfect opportunity to ask for a delay in payments.
Imagine you order a few shoe containers from China to deliver to Europe. The cargo would take circa 45 days to be delivered.
If you could agree with your supplier to pay on the 60th day, wouldn’t this help your cash flow? The answer is undoubtedly “YES”.
Likewise, in a well-established business relationship, the buyer could ask for longer instalments. Trade finance solutions like import and export finance help stabilise a business’s cash flow in this case.
Essentially, trade finance supports a business’s end-end supply chain process. Find out how traders finance their supply chain cycle through supply chain finance.
Brought to you by Velotrade, a marketplace for corporates to access financing.
Like our content? Follow us!
How does trade finance support the business growth of different industries?
Find out through some real financing case studies!
Trade Finance Players
Well, obviously there must be a buyer and a seller for any transaction to happen. However, a trade finance transaction could involve several other players.
Let’s find out!
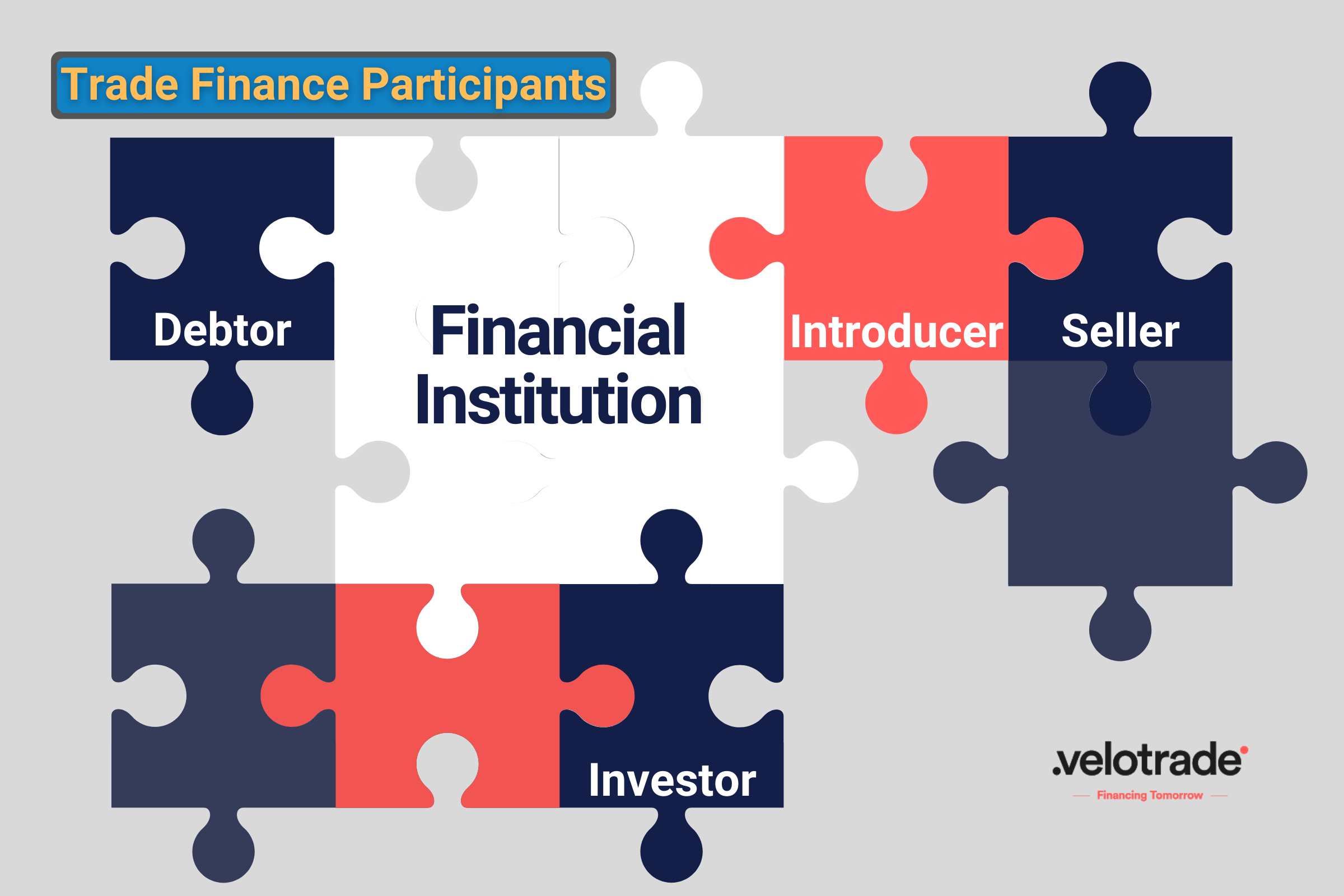
The Buyer A.K.A the Debtor
The buyer is the entity purchasing goods from the supplier. This is the company seeking funds to finance its business operations. Thus, by definition, a buyer is the debtor owing to the supplier.
Hence, he is legally obliged to pay the debt to the counterparty, known as the creditor.
In trade finance, the debtor is responsible for paying back funds to the lending company.
The Seller
The seller or the supplier is the company producing goods. The seller often engages in international trade activities selling his products abroad.
He owns the rights to the invoice payments owed by the debtor.
In trade finance, the seller is the pillar of the origination stage. Origination is where the invoices, receivables and other credit rights are “originated.”
Financial Institution
In trade finance, financial institutions are companies advancing funds to businesses. These include traditional lenders like banks and alternative lenders like FinTech.
While traditional institutions use their capital to grant funds, alternatives have a pool of liquidity providers willing to offer capital.
The institution must hold the required licenses to provide funding. While requirements vary from jurisdiction, there are some global requisites. For example, money lending, anti-money laundering, and counter-terrorist financing licenses that enable institutions to handle money legally.
So, how is the funding provided?
Well, traditional institutions like banks issue a Letter of Credit (LC) to the exporter on behalf of the importer. This document pledges the payment to be made by a certain due date.
The exporter must show proof of shipment to the bank by providing the bill of lading and other relevant shipping documents. This protects the transaction from any non-shipment and non-payment risks.
Relevant Incoterms are pre-agreed in the contract that defines the point of risk origination and the party liable for the loss. The latest 2020 update has 11 trade terms defined for buyers and sellers.
Know how Incoterms impact trade finance deals to understand its importance in the transaction.
However, these traditional lenders lengthen the already long and tedious financing process with their bureaucracy and lengthy due diligence.
This is where alternative lenders come into play.
Fintechs are paving the way with their fully digital financing process. Their less stringent requirements broaden credit access to SMEs.
Exporters and importers can receive capital within a few weeks or even days. This supports their high deal frequencies by providing them with a fast turnaround cycle. Thus, expanding their importing and exporting capacities.
Want to know more about the benefits of alternative financiers? Read more on how fintech beats traditional systems.
So, where do alternatives get this liquidity from?
Investors
These alternatives have a pool of investors willing to offer their excess liquidity in return for a yield.
They can be hedge funds, high net-worth individuals or indeed banks looking for alternative sources of yield.
Trade finance assets enhance investor returns with their short tenor and low correlation to traditional assets. Investors with different risk appetites are sourced to meet the different financing needs of borrowers.
Financial Intermediaries
There are many agents (brokers) supporting the various parties in a trade finance transaction.
These brokers earn commissions by helping the parties communicate and negotiate. This brokerage fee can either be a percentage or a fixed rate of the notional amount.
Here are some common brokers accessed by businesses in the global trade finance market.
Insurance Brokers
They help clients find insurance providers and assist in the underwriting of the contract.
For example, expensive microchips need insurance coverage for unforeseen events during transportation. Thus, the buyer and seller would like to underwrite insurance to protect the microchips from any damage.
Ship and Freight Brokers
These brokers play an essential role in the early tiers of the supply chain.
They move raw materials and goods across continents. Hence, facilitating international commerce and import & export activities.
For example, commodity traders (iron ore, coal, soybeans, sugar) work with shipbrokers to find cargo for their load. Likewise, containership brokers match containers (goods) with vessels (forwarders) to deliver goods globally.
Moreover, adding relevant trade terms can protect involved parties from potential damages. Find out how Incoterms 2020 identifies risk along the shipping process.
Introducers
Introducers connect SMEs or liquidity providers with financing institutions.
These can be agents or individuals with suitable contacts. Thus, their strength relies on their networking abilities.
They do not have the licenses and capabilities to operate as lending agents. Hence, they rely on their broad portfolio of wealthy individuals, hedge funds and family offices to generate revenues.
![]() Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Trade Finance Reduces Counterparty Risk
The strong KYC and due diligence performed by the financier mitigate the non-shipment and non-payment risks from the buyer or seller. - 3 Main Parties are Needed to Complete a Trade Finance Transaction
- The seller seeking financing
- The financier lending money
- The buyer who must repay the lender
- The Lender Can be a Traditional Financial Institution or an Alternative FinTech
While traditional institutions use their balance sheet’s capital to grant funds, alternatives use investors’ money. - A 4th Party Known as a Financial Intermediary May Sometimes be Involved
Borrowers may connect to agents or brokers to protect their goods from any unforeseen damage or losses
Who Can Use Trade Finance Solutions?

No matter how large the business is, most companies seek trade finance solutions.
Waiting is usually not an issue for large suppliers. They have different liquidity sources and a streamlined cash flow. Yet the additional working capital helps them meet frequent trade deals, keeping their business afloat.
In contrast, smaller suppliers struggle to withstand payment terms. Their cash lifecycle is short and the money gets in and out quickly.
These businesses could be traders from various industries like:
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Automobile and Transportation
- Financial institutions
…and the list goes on!
6 Types of Trade Finance Solutions
Now that you know all about how trade finance works, you might be curious to know what the solutions are.
Although the ultimate goal of each solution is to provide financing, there are 6 main types to fulfil the different needs of businesses.
Invoice Financing
Being one of the most popular forms of financing, invoice financing is where the seller obtains cash advance on invoices due at a future date. The debtor owes the financing company instead of the seller in this case.
While big banks like Barclays, HSBC, Hang Seng, and O.C.B.C offer invoice financing, several alternatives entering the market are helping businesses grow with this facility.
The process of invoice financing is explained clearly in our guide curated by experts.
Purchase Order Financing
PO financing finances the pre-shipment part of a business’s supply chain process. The purchase order works as the collateral in this case, as funds are granted based on the PO issued by the buyer.
Know the pros and cons of purchase order financing with a business example supported by cost breakdowns for a thorough understanding.
Supply Chain Financing
Supply chain finance (SCF) finances the post-shipment part of the supply chain process, covering a business’s end-end supply chain cycle.
It helps unlock funds tied in supply chain tiers like forwarding, intermediaries, and other parties involved. This adds efficiency to the import-export activities in trade finance.
Realise the value of finance in supply chain management to know why it could be vital for your business growth.
Working Capital Financing
Working capital financing is a perfect solution to fulfil a business’s short-term needs. Businesses seeking capital backed without an invoice or purchase order can opt for this solution.
The facility finances a business’s day-day operations to help them meet seasonal demands and cash flow requirements.
Unveil the benefits of working capital financing to know how it could grow your business regardless of whether you are facing cash flow issues or not.
Ecommerce Financing
Ecommerce financing is the latest addition to the trade finance products list. Following the increased demand for marketplaces like Lazada, eBay, Alibaba, JD, Taobao and Amazon, alternative financiers created the eCommerce finance solution.
Find out how eCommerce finance helps online sellers attain liquidity to close their eCommerce cash cycle gap.
Letter of Credit
The letter of credit is a document issued by a bank. Letter of credit is a well-known, widely used trade finance instrument. It adds protection to international trading activities.
There are several letters of credit available, depending on if for personal purposes or business requirements.
Velotrade goes beyond the above products by offering customised solutions to meet every business need.
Hassle-Free
Paper-Free
Stress-Free
Receive payments before invoice due dates efficiently with Velotrade's financing solutions.